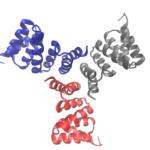
Cyclic proteins that assemble from multiple identical subunits (homo-oligomers) play key roles in many biological processes, including enzymatic catalysis and function and cell signaling. Researchers in the Molecular Biophysics and Integrated Bioimaging (MBIB) Division worked with University of Washington’s David Baker, who led a team to design in silico and crystallize self-assembling cyclic homo-oligomer proteins.
Researchers Gain Insight into Protein Critical to Zika Virus Reproduction
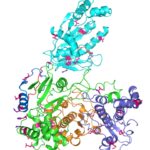
Zika virus is a mosquito-borne infectious disease linked to certain birth defects in infants in South and Central America and the United States. A Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) researcher, Banumathi Sankaran, worked as part of a multi-institutional team led by Cheng Kao, professor at Indiana University, and Pingwei Li, associate professor at Texas A&M University (TAMU), to map a key viral protein called NS5. Necessary to virus reproduction, NS5 contains two enzyme activities: one reduces the body’s ability to mount an immune response against infection and the other helps start the genetic replication process.
Designing Protein Cavities from Curved Beta Sheets
Curved beta sheets are important for the architecture of protein cavities, such as enzyme active sites and ligand-binding pockets. Beginning by analyzing classic protein formations and running folding simulations, University of Washington (UW) researchers under the leadership of David Baker designed six protein folds inspired by naturally occurring protein superfamilies. A research report published in the January 13 issue of Science describes how a multi-institutional team of scientists compared the predicted models to physical structures of these designed proteins.
Three Is Not a Crowd: Designed Metalloprotein Trimer Provides Stable Platform for Further Development
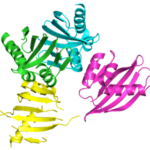
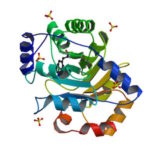 University of Washington (UW) researchers have designed a novel protein with properties that could lead to the generation of new photoactive proteins. This three-fold symmetric, self-assembling protein homotrimer contains a highly stable noncanonical amino acid. Noncanonical amino acids are not found among the 20 encoded amino acids in the body and can contain modifications to allow for new functionality. In this case, this amino acid contains a bipyridine group that chelates metal, thereby introducing new photochemical properties into the protein interface, and nucleating the formation of the homotrimer.
University of Washington (UW) researchers have designed a novel protein with properties that could lead to the generation of new photoactive proteins. This three-fold symmetric, self-assembling protein homotrimer contains a highly stable noncanonical amino acid. Noncanonical amino acids are not found among the 20 encoded amino acids in the body and can contain modifications to allow for new functionality. In this case, this amino acid contains a bipyridine group that chelates metal, thereby introducing new photochemical properties into the protein interface, and nucleating the formation of the homotrimer.
An article published last month in PNAS describes this work from a team of scientists led by David Baker at UW, which included Jose Henrique Pereira, Banumathi Sankaran, and Peter Zwart of the Molecular Biophysics & Integrated Bioimaging Division (MBIB). The MBIB scientists developed the crystal screen that was used to crystallize the novel protein and performed X-ray crystallography on Beamline 8.2.1 in the Berkeley Center for Structural Biology at the Advanced Light Source. Their X-ray crystallographic analysis of the homotrimer showed that the design process had near-atomic-level accuracy, demonstrating that computational protein design together with the utilization of noncanonical amino acids could be used to generate novel protein functions. These methods could be used to develop new therapeutics, biomaterials, and metalloproteins with useful optical or photochemical properties.
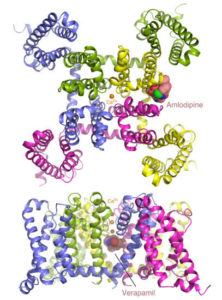
Two Basic Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Drugs
Calcium channel blockers are widely prescribed for heart and blood-vessel diseases. With the help of the high-intensity x-ray beams and remotely controlled robots at the Advanced Light Source (ALS), two groups of scientists from University of Washington have revealed, at atomic resolution, how two different classes of calcium channel blocker drugs produce their therapeutic effects. The researchers took advantage of the remotely controllable robot automounter available in the Berkeley Center for Structural Biology at the ALS to screen a large number of crystals for the best diffraction. The tunable x-ray source also allowed them to collect anomalous diffraction data at Beamlines 8.2.1 and 8.2.2 with bromine-incorporated drugs, which was critical for locating the drug molecules in the crystal. The results pave the way for optimizing these classic compounds for safer and more reliable pharmaceutical applications. Read the ALS Science Highlight.
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- Next Page »
Was this page useful?