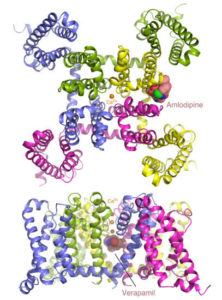
Calcium channel blockers are widely prescribed for heart and blood-vessel diseases. With the help of the high-intensity x-ray beams and remotely controlled robots at the Advanced Light Source (ALS), two groups of scientists from University of Washington have revealed, at atomic resolution, how two different classes of calcium channel blocker drugs produce their therapeutic effects. The researchers took advantage of the remotely controllable robot automounter available in the Berkeley Center for Structural Biology at the ALS to screen a large number of crystals for the best diffraction. The tunable x-ray source also allowed them to collect anomalous diffraction data at Beamlines 8.2.1 and 8.2.2 with bromine-incorporated drugs, which was critical for locating the drug molecules in the crystal. The results pave the way for optimizing these classic compounds for safer and more reliable pharmaceutical applications. Read the ALS Science Highlight.
Thank you for visiting our newly redesigned website. Please complete this quick survey to let us know your thoughts.
Was this page useful?
Send