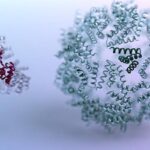
The SIBYLS beamline at the Advanced Light Source was used to characterize proteins dreamt up by a reinforcement learning algorithm. The algorithm, developed by researchers in David Baker’s lab at the University of Washington, is powered by the machine learning strategy behind computer programs capable of defeating top human players at board games like chess and go. The advance could create a pathway to greater control when designing therapeutic proteins, vaccines, and other molecules.
Sauer Leaves Legacy in Science and Teaching
As a young man, Kenneth Sauer joined Berkeley Lab four years after arriving in Berkeley for his postdoctoral position with famed chemist Melvin Calvin. By that time, he had accepted an assistant professorship in UC Berkeley’s Department of Chemistry to continue what would be his life’s scientific work on the intricate physical process of photosynthesis. He remained active for over 50 years and was, most recently, a professor emeritus of chemistry at UC Berkeley. Sauer died at the age of 91 following a brief illness on November 6, 2022.
Nogales Named 2023 Shaw Prize Laureate
Biophysicist Eva Nogales, a senior faculty scientist in the Molecular Biophysics and Integrated Bioimaging Division, is a 2023 recipient of the Shaw Prize in Life Science and Medicine. Nogales, who is also a UC Berkeley distinguished professor of biochemistry, biophysics, and structural biology, shares the prize with Patrick Cramer of the Max Planck Institute for Multidisciplinary Sciences in Germany. The pair were honored for pioneering structural biology techniques that enabled visualization of the protein machines responsible for gene transcription at the level of individual atoms.
Researchers Capture Elusive Missing Step in Photosynthesis
After decades of effort, scientists have revealed atomic-scale details of the water splitting step of photosynthesis, the chemical process that generates the air we breathe. The latest work adds to our understanding of photosynthesis and will aid the development of fully renewable alternative energy sources.
Gemini Beamline Banks First Protein Structure
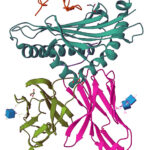
A protein structure obtained at Beamline 2.0.1 (“Gemini”) at the Advanced Light Source (ALS) has recently been published in the literature and deposited into the Protein Data Bank—two significant firsts for this beamline. The structure helped provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms involved in triggering certain inflammatory diseases. This milestone, which utilized Gemini’s capacity to target crystals smaller than 20 microns, was almost a decade in the making. Simon Morton, now a semi-retired staff scientist at ALS, and Corie Ralston, facility director at the Molecular Foundry and a staff scientist in the Molecular Biophysics and Integrated Bioimaging Division (MBIB), helped bring the microfocus beamline to the Berkeley Center for Structural Biology (BCSB) in 2014. Beamline operations are now led by Marc Allaire, a biophysicist staff scientist in MBIB and head of the BCSB.
Read More in the Berkeley Lab News Center.
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- …
- 75
- Next Page »
Was this page useful?