Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) will partner with four clean energy small businesses to accelerate the commercialization of their innovative bioenergy, buildings and vehicle technologies as part of the Small Business Vouchers (SBV) pilot launched in July 2015 by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). One of those businesses is Lygos, Inc., a local business that has partnered with the Advanced Biofuels Process Demonstration Unit (ABPDU) in the past to achieve pilot-scale production of malonic acid from sugar. Lygos will conduct the necessary testing at the APBDU to overcome current barriers to scale-up, and then move production to the large-scale fermenters at DOE’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Read more at the Berkeley Lab News Center.
DOE-funded Bioenergy Research Centers File 500th Invention Disclosure
 Three U.S. Department of Energy-funded research centers – the BioEnergy Science Center (Oak Ridge National Laboratory), the Great Lakes Bioenergy Research Center (University of Wisconsin–Madison and Michigan State University), and the Joint BioEnergy Institute (Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory) – are making progress on a shared mission to develop technologies that will bring advanced biofuels to the marketplace, reporting today the disclosure of their 500th invention. Read more on the JBEI website.
Three U.S. Department of Energy-funded research centers – the BioEnergy Science Center (Oak Ridge National Laboratory), the Great Lakes Bioenergy Research Center (University of Wisconsin–Madison and Michigan State University), and the Joint BioEnergy Institute (Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory) – are making progress on a shared mission to develop technologies that will bring advanced biofuels to the marketplace, reporting today the disclosure of their 500th invention. Read more on the JBEI website.
Antioch High School Takes Part in Mock Interviews at Biosciences ESOC
Antioch High School juniors practiced their job application skills on February 26 during mock interviews held at LBL’s Biosciences Emery Station Operations Center (ESOC). The students, who are taking part in the Biotech Partners program, are getting ready for their interviews in order to get summer internships. The ESOC operations staff was on hand to … Read more »
New Way to Reduce Plant Lignin Could Lead to Cheaper Biofuels
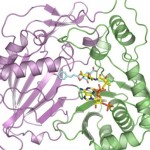
Aymerick Eudes and Dominique Loqué of the Joint Bioenergy Institute (JBEI) led a study that shows for the first time that an enzyme can be tweaked to reduce lignin in plants. Their technique could help lower the cost of converting biomass into carbon-neutral fuels to power your car and other sustainably developed bio-products. The crystal structure of this enzyme was solved using data collected in the Berkeley Center for Structural Biology at the Advanced Light Source. Read more on the Berkeley Lab News Center.
JBEI Invention Leads to More Efficient Biofuel Production for Industrial Application
New Biosynthesis Pathways for Five-Carbon Alcohol from Mevalonate Are Available For Licensing
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)’s Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI) have developed two novel biosynthesis pathways for five-carbon alcohol (isopentenol or 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol) from mevalonate that reduce the energy demand and cost of earlier applications of the mevalonate pathway by using genetically engineered host cells, whose culturing stage can happen both in anaerobic or aerobic conditions. This invention can be used in an industrial scale, even under oxygen-limited conditions. These modified pathways would be a good platform for industrial production of isopentenol which is a potential gasoline alternative and a precursor of commodity chemicals such as isoprene. Read more on the JBEI website.
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- …
- 62
- Next Page »
Was this page useful?