Researchers at Berkeley Lab and their collaborators who work on the Phenix software suite have published a new paper that summarizes how to determine three-dimensional macromolecular structures from three experimental methods: X-ray crystallography, neutron diffraction, and electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM). The workflow is similar for these techniques, but there are nuances for each method. In particular, the paper describes the most recent developments in Phenix, which include tools to build, validate, and refine cryo-EM structures, which have accounted for the majority of large macromolecular structures deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) since 2015.
 The article appeared in the journal Acta Crystallographica Section D: Structural Biology and is featured on the cover of the October 2019 issue. An accompanying commentary provides a review of some of the new tools, concluding that “taken together, the latest features of Phenix are not only convenient for full workflows but also respond to specific needs, depending on the applications and user expertise.”
The article appeared in the journal Acta Crystallographica Section D: Structural Biology and is featured on the cover of the October 2019 issue. An accompanying commentary provides a review of some of the new tools, concluding that “taken together, the latest features of Phenix are not only convenient for full workflows but also respond to specific needs, depending on the applications and user expertise.”
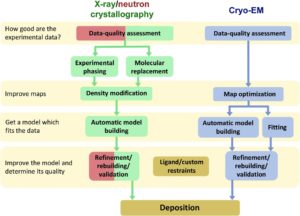 Tasks performed within Phenix include data-quality assessment, map improvement, model building, the validation/rebuilding/refinement cycle, and deposition. Each tool caters to the properties of the experimental data. The program design emphasizes automation wherever possible to minimize repetitive and time-consuming manual tasks, while default settings encourage best practices. The user-friendly graphical user interface provides access to major tasks and streamlines the transition between programs, project tracking, and re-running of previous tasks.
Tasks performed within Phenix include data-quality assessment, map improvement, model building, the validation/rebuilding/refinement cycle, and deposition. Each tool caters to the properties of the experimental data. The program design emphasizes automation wherever possible to minimize repetitive and time-consuming manual tasks, while default settings encourage best practices. The user-friendly graphical user interface provides access to major tasks and streamlines the transition between programs, project tracking, and re-running of previous tasks.
Molecular Biophysics and Integrated Bioimaging (MBIB) Division Director Paul Adams leads the group of scientists at Berkeley Lab, as well as the overall collaboration that includes the New Mexico Consortium (NMC), Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL), Duke University, and the University of Cambridge, who develop Phenix. Pavel Afonine, Dorothee Liebschner, Nigel Moriarty, Billy Poon, and Oleg Sobolev develop Phenix at Berkeley Lab under Adams’s direction. The other group leads are: Tom Terwilliger, NMC/LANL; Jane and David Richardson, Duke; and Randy Read, Cambridge. Additional collaborators on this paper are affiliated with Baylor College of Medicine and Institute of Genetics and Molecular and Cell Biology (IGBMC) in France.
Phenix is funded by the National Institutes of Health General Medical Sciences and the Phenix Industrial Consortium.