Previous work on microbial mats had primarily relied on culturing virus and host pairs in the laboratory to study their interactions. In The ISME Journal, a team co-led by JGI postdoctoral researcher Mária Džunková used single-cell sequencing to sequence both a cell’s genome and detect accompanying viral sequences, which would suggest the virus had been infecting the cell. Read the full story on the JGI website.
JGI Scientists Pen Genome Watch Articles
Tanja Woyke and other JGI researchers made their debut writing for a column of the prestigious scientific research magazine Nature Reviews Microbiology last year — and there’s more to come in 2020. In 2018, Woyke received a message from Andrea Du Toit, senior editor for Nature Reviews Microbiology, with an unusual opportunity: would JGI researchers consider regularly writing for the magazine’s column Genome Watch? The column appears in six issues of the monthly magazine each year.
Du Toit invited JGI to write half of the 2019 Genome Watch articles as a way to expose readers to a broader genomics perspective. Woyke spread the word among her JGI colleagues, and they agreed, providing three articles for the journal with Du Toit as their editor. The partnership has proven so successful this year, JGI is providing another three Genome Watch articles. Go here to read the blog post on the JGI website.
JGI-Led Team Expands the Global Diversity of Large and Giant Viruses
In Nature, a team led by JGI researchers reported uncovering a broad diversity of large and giant viruses that belong to the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses (NCLDV) supergroup. The expansion of the diversity for large and giant viruses offered the researchers insights into how they might interact with their hosts, and how those interactions may in turn impact the host communities and their roles in carbon and other nutrient cycles. Read more on the JGI website.
JGI Develops “Hook and Bait” Single-Cell Genomic Approach to Bioprospecting
One of the most vital pieces of equipment for fly fishing is a boxful of lures. Designed with feathers or wires to mimic an insect or a particular movement, each of these lures are the bait designed to attract specific catches. A similar “hook and bait” technique has been developed by researchers led by JGI Microbial Program Head Tanja Woyke. Using a single-cell screen, they can now identify microbes with specific functional characteristics. When they tested the screen method on a microbial community from geothermal hot springs, they uncovered a novel cellulose-degrading bacterium typically found in low abundances. Read more on the JGI website.
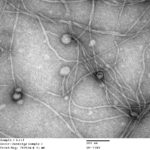
JGI Overhauls Perception of Inovirus Diversity
Inoviruses are filamentous viruses with small, single-stranded DNA genomes and a unique chronic infection cycle. In Nature Microbiology, a team led by DOE Joint Genome Institute (JGI) researchers applied machine learning to publicly available microbial genomes and metagenomes to search for inoviruses. The search tool combed through more than 70,000 microbial and metagenome datasets, ultimately identifying more than 10,000 inovirus-like sequences compared to the 56 previously known inovirus genomes. The results revealed inoviruses are in every major microbial habitat—including soil, water, and humans—around the world.
“We’re not sure why we systematically manage to miss them; maybe it’s due to the way we currently isolate and extract viruses,” said the study’s lead author Simon Roux, a JGI research scientist in the Environmental Genomics group. Click here to read the full story on the JGI site.
Was this page useful?