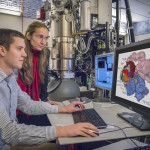
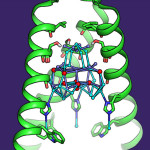
Using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory faculty scientist Eva Nogales and her team have made a significant breakthrough in our understanding of how our molecular machinery finds the right DNA to copy, showing with unprecedented detail the role of a powerhouse transcription factor known as TFIID. Read more at the Berkeley Lab News Center.
Doudna receives Canada’s Gairdner Award as CRISPR sweeps field
Jennifer Doudna, a faculty scientist in the Molecular Biophysics & Integrated Bioimaging Divison, as well as professor of molecular and cell biology and of chemistry at UC Berkeley, will share the 2016 Canada Gairdner International Awards with four others for their roles in discovering and re-engineering the CRISPR-Cas9 system to create today’s most-talked-about genetic tool. Read more at UC Berkeley NewsCenter.
X-ray Studies at SLAC and Berkeley Lab Aid Search for Ebola Cure
Recently, scientists from University of California, San Francisco, performed research at two national laboratories to determine protein structures that c0uld be the key to preventing Ebola infection. Alexander Kintzer and Robert Stroud, used two structural biology beamlines (5.0.2 and 8.3.1) at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source, to determine in atomic detail how a potential drug molecule fits into and blocks a channel in cell membranes that Ebola and related “filoviruses” need to infect victims’ cells. The study, published March 9 in Nature, marks an important step toward finding a cure for Ebola and other diseases that depend on the channel. Read more at the SLAC News Center.
Adams Named Division Director for Molecular Biophysics & Integrated Bioimaging
Jay Keasling, Associate Laboratory Director for Biosciences, has announced that Paul Adams has accepted the position of Division Director for the Molecular Biophysics & Integrated Bioimaging (MBIB) Division. Adams served as the MBIB Interim Division Director since the Biosciences Area re-organization took effect this past October 1 and has been instrumental in developing a strategic plan and leading the effort to launch the Division.
Improving Anti-Influenza Medications
The annual flu epidemics caused by influenza viruses, especially the influenza A virus, affect about 10–20% of the world’s population each season. This highly contagious illness can trigger serious complications and lead at times to death. A team of scientists led by Bill DeGrado from UC San Francisco have been studying the M2 proton channel from the influenza A virus, which is one of nature’s smallest proton-selective channels and a drug target for this virus. Protein crystallography performed at the Advanced Light Source (ALS) Beamline 8.3.1 helped scientists understand the M2 proton-channel structure and function, and will aid the design of better anti-influenza medications. Read the ALS Science Brief.
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- …
- 78
- Next Page »
Was this page useful?