The National Student Leadership Conference (NSLC) visited JBEI on July 17. NSLC is a nonprofit, nonpartisan, education organization which brings together high school students for fast-paced, high-level, interactive summer sessions. For a fifth year in a row JBEI and NSLC partnered to instruct students about the benefits and research behind biofuels and bioproducts.
The National Student Leadership Conference (NSLC) visited JBEI on July 17. NSLC is a nonprofit, nonpartisan, education organization which brings together high school students for fast-paced, high-level, interactive summer sessions. For a fifth year in a row JBEI and NSLC partnered to instruct students about the benefits and research behind biofuels and bioproducts.
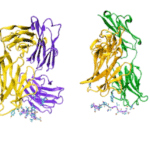
Structures Reveal New Target for Malaria Vaccine
With the aid of protein crystallography at the Advanced Light Source (ALS), investigators at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) and the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle led a study in which they isolated human-derived antibodies that protect against malaria and determined the antibodies’ site of attack. The team isolated the antibody, called CIS43, from the blood of a volunteer who had received an experimental vaccine made from whole, weakened malaria parasites (Plasmodium falciparum). The use of a whole-parasite vaccine allowed the isolation of antibodies against circumsporozoite protein (CSP), which covers the malaria parasite in its native conformation. The scientists co-crystallized CIS43 with various peptides from CSP. Protein crystallography at ALS Beamlines 5.0.1 and 5.0.2 revealed that CIS43 works by binding to a specific portion, or epitope, of CSP. This epitope occurs only once along the length of the surface protein and is conserved across 99.8 percent of all known strains of P. falciparum. The discovery paves the way for the development of a more effective and practical human vaccine for malaria, a disease responsible for half a million deaths worldwide each year.
Read more from the ALS.
Photos From Women @ The Lab Awards Ceremony
View photos from the July 9 Women @ The Lab awards ceremony, where six Biosciences Area staffers were among the outstanding group of female scientists, engineers, technicians, and operations professionals recognized.
KBase Flagship Paper Published in Nature Biotechnology
In a letter to the editor published July 6 in Nature Biotechnology, the KBase team presented a comprehensive overview of the platform and an assessment of its scientific impact. The paper describes the unique features and infrastructure of the platform, in addition to highlighting scientific use cases that demonstrate its significance for biology research.
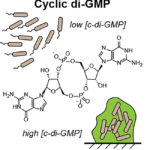
JGI Helps Develop Biosensors to Measuring Cyclic di-GMP in Bacteria
The molecule cyclic di-GMP is found in nearly all types of bacteria and interacts with cell signaling networks that control many basic cellular functions. It plays an important role in regulating microbial cellulose production and biofilm formation, which affects a number of environments, including plants, soil, and the gut. To better understand the dynamics of this molecule, researchers developed the first chemiluminescent biosensors for measuring cyclic di-GMP in bacteria through work enabled by the JGI’s Community Science Program (CSP).
Read the full highlight on the JGI website.
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- …
- 213
- Next Page »
Was this page useful?