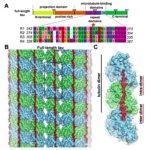
Researchers at Berkeley Lab and UC Berkeley have combined cutting-edge cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) with computational molecular modeling to produce a near atomic-resolution model of the interaction between microtubules—crucial components of eukaryotic cell ultrastructure—and microtubule-associated proteins called tau. The model provides insight into how tau stabilizes microtubules, and what makes it dissociate to form tau aggregates, or “tangles,” in some neurological diseases—including Alzheimer’s disease—generally referred to as tauopathies.
Biosciences Researchers Honored by the National Academy of Sciences
Three scientists affiliated with the Biosciences Area have been recognized by the National Academy of Sciences (NAS), one as the recipient of an NAS award and two as newly elected members. On Sunday, the NAS formally presented its 2018 NAS Award in Chemical Sciences to Jennifer Doudna, a faculty biochemist in the Molecular Biophysics and Integrated Bioimaging (MBIB) Division. Judith Campisi, a biochemist affiliated with Biological Systems and Engineering Division, Ehud “Udi” Isacoff, an MBIB faculty biologist, are among the group of 84 new members elected to the NAS.
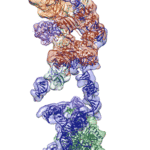
Cryo-EM Reveals Structure of Human Telomerase
Regulation of the enzyme telomerase has been implicated in cancer, other human diseases, and aging, but progress towards therapeutic manipulation of telomerase has been hampered by the lack of high-resolution structural data. Now, researchers in senior faculty scientist Eva Nogales’ lab in Molecular Biophysics and Integrated Bioimaging (MBIB), in collaboration with UC Berkeley professor of Biochemistry, Biophysics and Structural Biology Kathleen Collins, have published a paper in Nature describing the 3-D molecular structure of the human telomerase enzyme.
Biosciences Area FY18 LDRD Projects
The projects of 13 Biosciences Area scientists and engineers received funding through the FY18 Laboratory Directed Research and Development (LDRD) program. These projects span a diverse array of topics and approaches including the study of microbiomes in relation to patterns of mutualism, crop productivity, and gut health; synthetic biology for engineering biosurfactant production and energy conversion pathways; and the application of technologies such as machine learning, high-resolution optical microscopy, and single-cell transcriptomics. Together, these efforts account for 18.75 percent of the $20 million allocated. Lab-wide, 74 projects were selected from a field of 215.
Chan Zuckerberg Institute Funds Projects in Support of Human Cell Atlas
Two proposals, from Biosciences Area researchers Cynthia McMurray and Carolyn Larabell, have been recommended for funding by the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI) through a new grant program focused on developing collaborative computational tools to support the Human Cell Atlas (HCA). A global endeavor governed by an organizing committee co-chaired by Aviv Regev at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and Sarah Teichmann at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, the HCA will generate a variety of molecular and imaging data across a range of modalities and spatial scales. To advance the analysis, interpretation, and dissemination of these data, the CZI issued an open call in July 2017 for proposals aimed at creating new computational tools, algorithms, visualizations, and benchmark datasets. After a thorough evaluation process, CZI recommended 85 projects (out of nearly 300 submissions) for funding, and will provide $15 million in total over one year for their execution.
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- …
- 78
- Next Page »
Was this page useful?