JBEI develops new synthetic biology tools for engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae
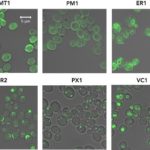
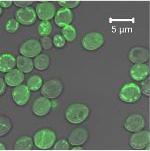 Pioneering work has been led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI) to engineer microbes to transform plant derived starting materials into energy-rich biofuels. But despite the progress in genomics and synthetic biology for the optimization of biofuel production in engineered microbes, microbial engineering methods remain slow and laborious. Such is the case of the fungal host, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The yeast S. cerevisiae has proven to be an excellent organism for commercial-scale production of biological molecules, though its strain development remains painstakingly slow due to difficulties related to the combined effect of different expression parts and host conditions. Now, researchers at JBEI have developed the largest, most comprehensive Cas9-based toolkit to quickly institute genetic changes in S. cerevisiae to optimize heterologous gene expression.
Pioneering work has been led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI) to engineer microbes to transform plant derived starting materials into energy-rich biofuels. But despite the progress in genomics and synthetic biology for the optimization of biofuel production in engineered microbes, microbial engineering methods remain slow and laborious. Such is the case of the fungal host, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The yeast S. cerevisiae has proven to be an excellent organism for commercial-scale production of biological molecules, though its strain development remains painstakingly slow due to difficulties related to the combined effect of different expression parts and host conditions. Now, researchers at JBEI have developed the largest, most comprehensive Cas9-based toolkit to quickly institute genetic changes in S. cerevisiae to optimize heterologous gene expression.