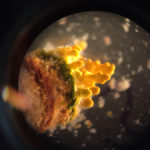
Previous work on microbial mats had primarily relied on culturing virus and host pairs in the laboratory to study their interactions. In The ISME Journal, a team co-led by JGI postdoctoral researcher Mária Džunková used single-cell sequencing to sequence both a cell’s genome and detect accompanying viral sequences, which would suggest the virus had been infecting the cell. Read the full story on the JGI website.
JGI Helps Conduct Antarctic Lake Time-Series Study
Through a decade-long time-series study recently reported in Microbiome, a team led by Rick Cavicchioli of Australia’s University of New South Wales and including JGI researchers found that light-harvesting bacteria in Antarctica’s Ace Lake defy the norm when it comes to nutrient cycling in polar regions. While microbial populations in other Antarctic lakes and the nearby Southern Ocean shift from phototrophs to archaea when sunlight becomes scant, Ace Lake’s bacteria instead go through a boom and bust cycle aligned with light availability. Read more on the JGI website.
JGI Scientists Pen Genome Watch Articles
Tanja Woyke and other JGI researchers made their debut writing for a column of the prestigious scientific research magazine Nature Reviews Microbiology last year — and there’s more to come in 2020. In 2018, Woyke received a message from Andrea Du Toit, senior editor for Nature Reviews Microbiology, with an unusual opportunity: would JGI researchers consider regularly writing for the magazine’s column Genome Watch? The column appears in six issues of the monthly magazine each year.
Du Toit invited JGI to write half of the 2019 Genome Watch articles as a way to expose readers to a broader genomics perspective. Woyke spread the word among her JGI colleagues, and they agreed, providing three articles for the journal with Du Toit as their editor. The partnership has proven so successful this year, JGI is providing another three Genome Watch articles. Go here to read the blog post on the JGI website.
Journal Paper Caps JGI Research Pilot with Florida High School
In 2018, JGI embarked on a pilot project with biology students from Boca Raton Community High School in Palm Beach County, Florida. The class sought to apply the latest molecular techniques to learn more about the microbial communities in the Arthur R. Marshall Loxahatchee National Wildlife Refuge, a 226-square mile area of the northern Everglades in Palm Beach County, and particularly about the microbes that play roles in the methane cycle. Their data report, which provides the only known reference microbiome data sets for the Loxahatchee Refuge, was published in the journal Environmental Microbiome. Read more on the JGI website.
A Community-driven Data Science System to Advance Microbiome Research
The National Microbiome Data Collaborative will develop an open-access framework for harnessing microbiome data to accelerate discoveries
The National Microbiome Data Collaborative (NMDC), a new initiative aimed at empowering microbiome research, is gearing up its pilot phase after receiving $10 million of funding from the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science. Led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), in partnership with Los Alamos (LANL), Oak Ridge (ORNL), and Pacific Northwest (PNNL) National Laboratories, the NMDC will leverage DOE’s existing data-science resources and high-performance computing systems to develop a framework that facilitates more efficient use of microbiome data for applications in energy, environment, health, and agriculture.
Was this page useful?