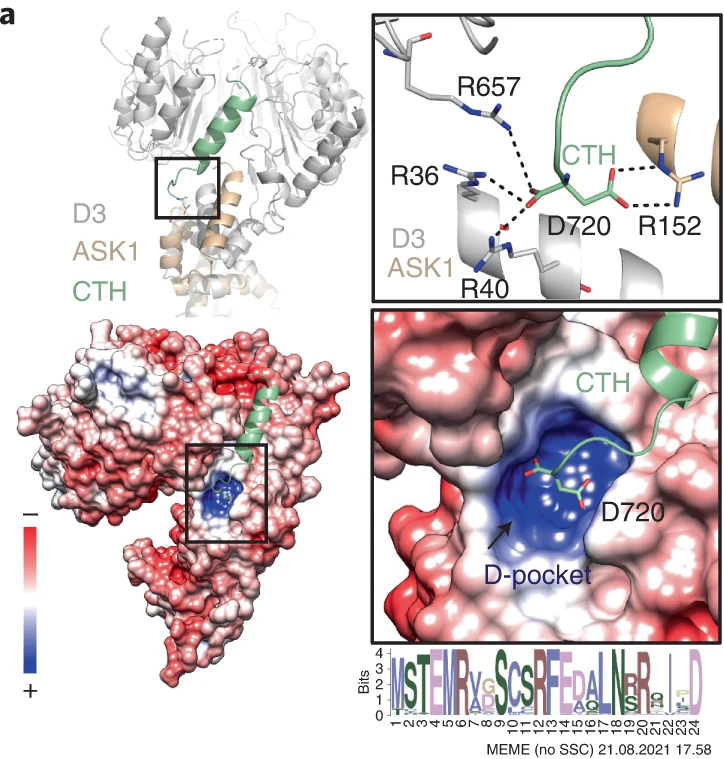
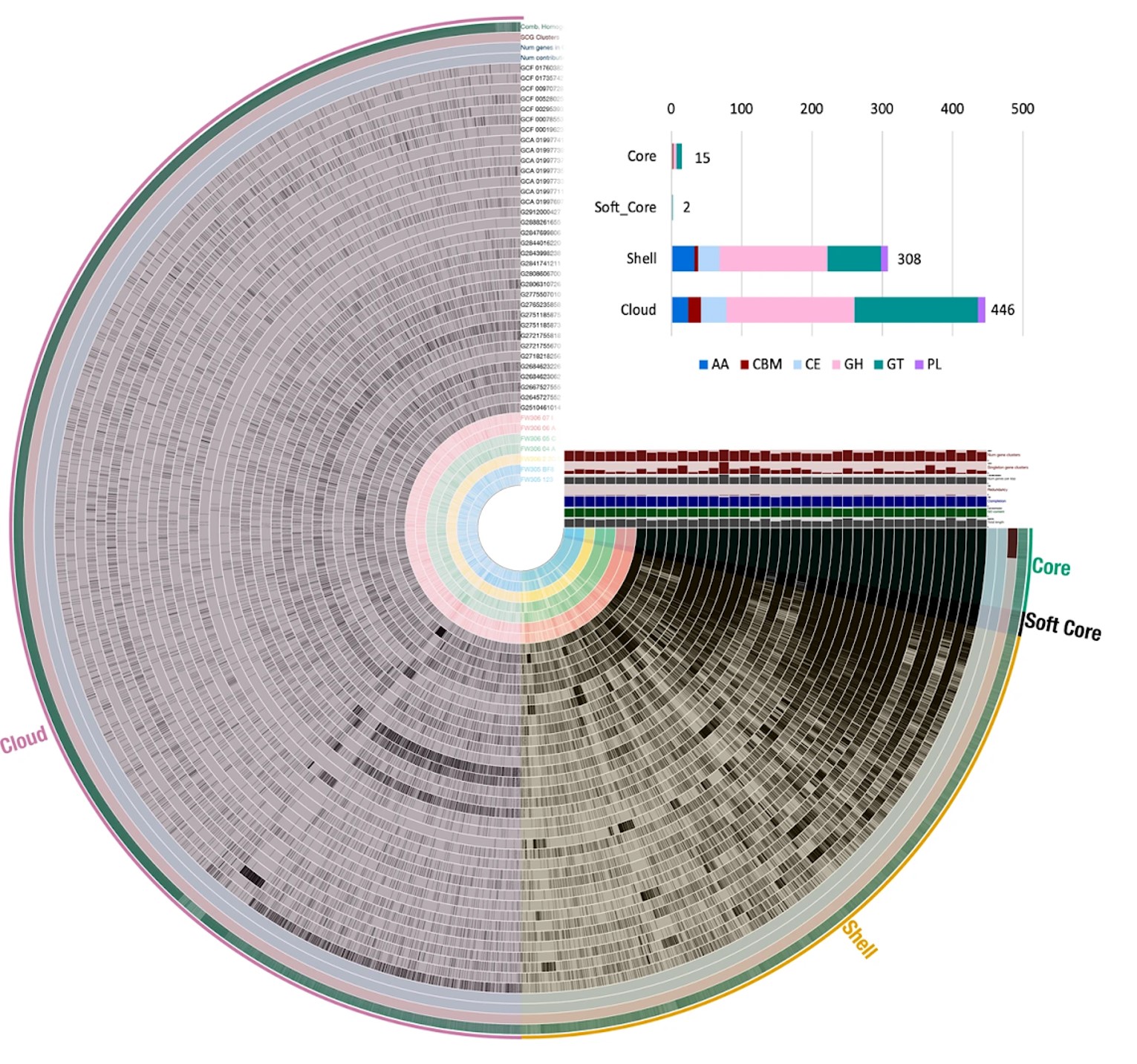
Biosciences Researchers Part of Genomic Analysis of Giant Bacteria Found in Guadeloupe Mangroves

In Science, a team led by Jean-Marie Volland, a scientist with joint appointments at the DOE Joint Genome Institute (JGI) and the Laboratory for Research in Complex Systems, and Silvina Gonzalez-Rizzo and Olivier Gros of the Université des Antilles, described the morphological and genomic features of a giant filamentous bacterium, along with its life cycle.
More »