 In a Metabolic Engineering Communications paper entitled “Enhanced fatty acid production in engineered chemolithoautotrophic bacteria using reduced sulfur compounds as energy sources” researchers at the Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI) have demonstrated a promising biological approach to convert nuisance chemicals in municipal wastewater (sewage) treatment plants into renewable fuels or chemicals. Read more on the JBEI website.
In a Metabolic Engineering Communications paper entitled “Enhanced fatty acid production in engineered chemolithoautotrophic bacteria using reduced sulfur compounds as energy sources” researchers at the Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI) have demonstrated a promising biological approach to convert nuisance chemicals in municipal wastewater (sewage) treatment plants into renewable fuels or chemicals. Read more on the JBEI website.
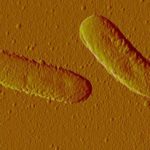
Study Finds Molecular Switch That Triggers Bacterial Pathogenicity
Scientists have revealed that the supercoiling of bacterial chromosomes around histone-like proteins can trigger the expression of genes that make the microbe invasive. The discovery could provide a new target for the development of drugs to prevent or treat bacterial infection.
The study lead author Michal Hammel, research scientist in the Molecular Biophysics & Integrated Bioimaging (MBIB) Division, teamed up with MBIB faculty scientist Carolyn Larabell; both are pictured above. Read more on the Berkeley Lab News Center.
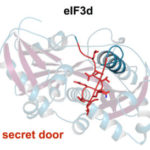
When Targeting Cancer Genes, Zero in on the One Percent
UC Berkeley researchers have found a promising new drug target within the pathway that controls production of a cell’s thousands of proteins. That is appealing, in part, because it appears to control production of only a few percent of the body’s many proteins, those critical to regulating the growth and proliferation of cells. The study was led by Jamie Cate, a faculty scientist in Berkeley Lab’s Molecular Biophysics & Integrated Bioimaging Division. Read more on UC Berkeley News.
JBEI Scientists Harness CO2 to Consolidate Biofuel Production Process
 JBEI scientists have shown that adding carbon dioxide gas during the deconstruction phase of biofuel production successfully neutralized the toxicity of ionic liquids. The technique, which is reversible, allows the liquid to be recycled, representing a major step forward in streamlining the biofuel production process. Read more on the Berkeley Lab Newscenter
JBEI scientists have shown that adding carbon dioxide gas during the deconstruction phase of biofuel production successfully neutralized the toxicity of ionic liquids. The technique, which is reversible, allows the liquid to be recycled, representing a major step forward in streamlining the biofuel production process. Read more on the Berkeley Lab Newscenter
The Bloody Battle Against Aging
By examining the chemical makeup of young blood, bioengineers, including David Schaffer, faculty engineer in the Molecular Biophysics and Integrated Bioimaging Division, have discovered a drug that could turn back the age clock. Read more in the Berkeley Science Review.
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- …
- 213
- Next Page »
Was this page useful?