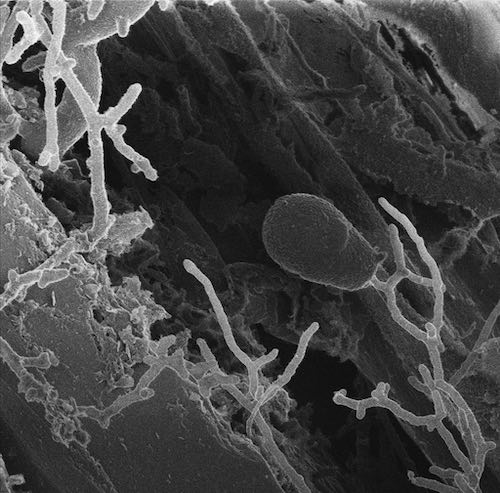
Anaerobic fungi, which die in the presence of oxygen, thrive in herbivore guts and help them digest their host’s last leafy meal. In their evolutionary history, these fungi branched off early from aerobic fungi, which can breathe oxygen — just like we do. Oxygen is a rich source of energy, and because anaerobic fungi can’t harness it, scientists long held that these fungi don’t have the energy to make complex compounds called natural products. Yet, analyzing the genomes and genome products of four anaerobic fungal species has revealed that this group is unexpectedly powerful: they can whip up dozens of complex natural products, including new ones.
The work was partly enabled by the “Facilities Integrating Collaborations for User Science” (FICUS) collaborative science initiative between the JGI and the Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory.
Read the full science highlight on the JGI website.