By advancing data science and computing for biology, we can increase the reproducibility efficiency, and effectiveness of national research and development. We will accelerate experimentation by integrating technologies, and we will work to translate new technologies into the commercial sector for societal and economic benefit. We aim to grow next-generation omics and gene-editing tools, as well as develop hardware to support and understand biology, thereby enabling scientific advances in biology for improved health, sustainable energy options, and a resilient environment. We will develop and maintain capabilities that can pivot to addressing urgent national needs.

Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Leveraging our team science heritage, we integrate biosciences, engineering computing, and data sciences to develop pioneering AI/ML models.
Data Science
Securing, making accessible, and organizing some of the most vital datasets for understanding the complexities of human health, the foundations of ecosystems, and the next generation of bio-based materials and energy sources.
Modeling
Gaining insight from large data sets and developing new simulation tools for science using high-performance computing and machine learning.
Omics and Gene Editing
Employing DNA synthesis, genome engineering, and synthetic
biology methods to engineer organisms for research and industrial application and to accelerate discovery.
Fabricated Ecosystems
Using fabricated ecosystems of different scales to study how soil-plant-microbe interactions and bridge the gap between lab and field research, transform our ability to quantify and predict behaviors, and make ecosystem experiments reproducible.
Structural Biology and Imaging
Utilizing light microscopy, cryo-electron microscopy, X-ray crystallography, and X-ray tomography to reveal insights into biological structures such as plant roots, organelles, proteins, and therapeutic targets.
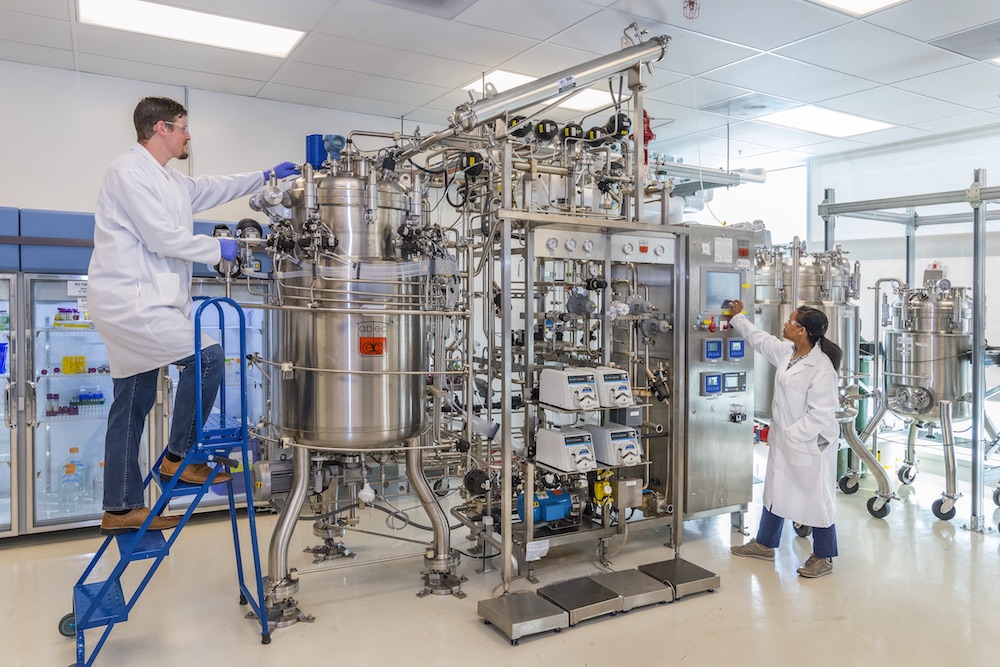

The ABPDU is a state-of-the-art facility for testing and developing emerging biofuels, bio-based chemicals, and biomaterial technologies in a process demonstration production environment.
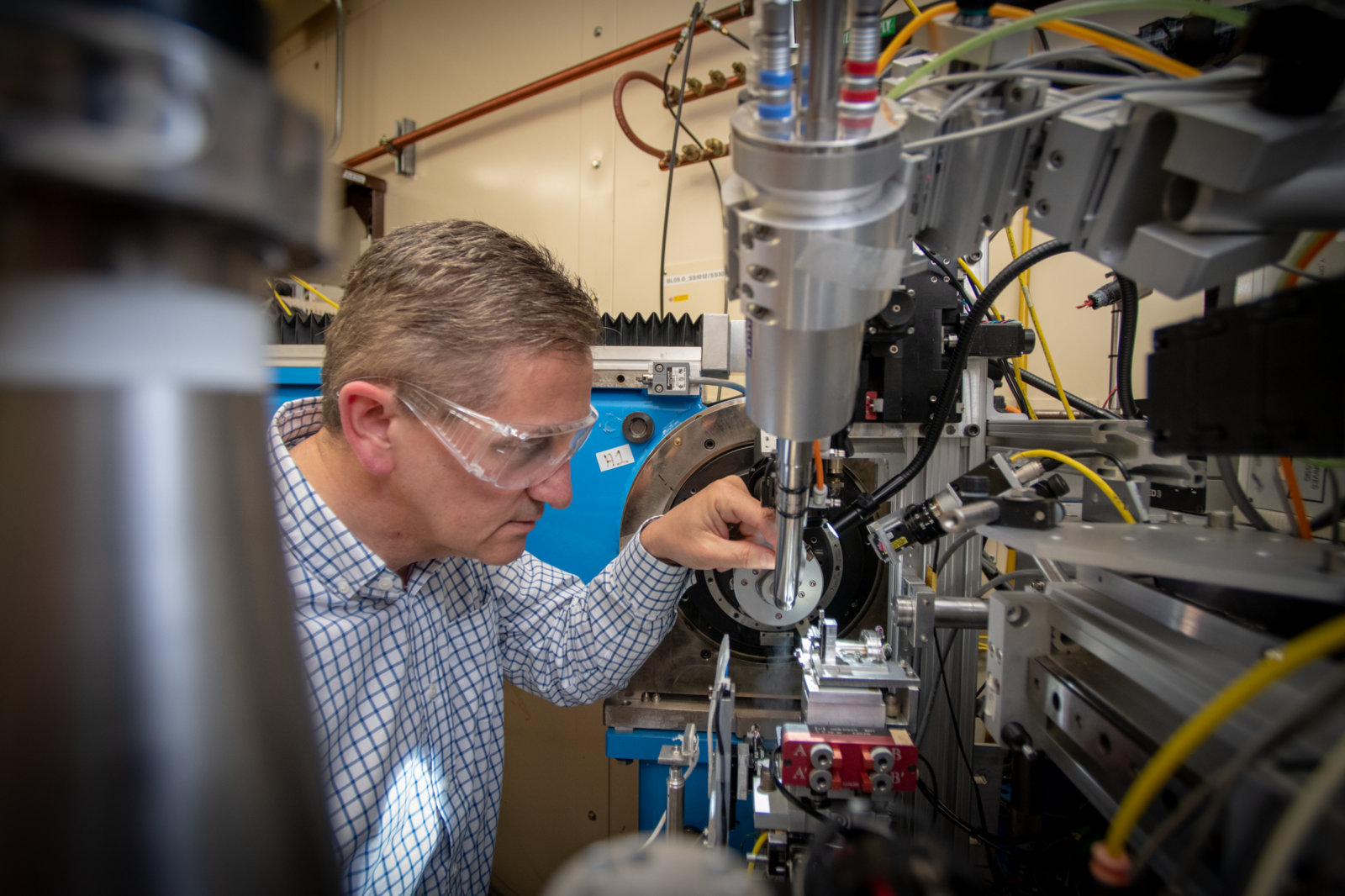
Several X-ray beamlines at the Advanced Light Source (ALS) are dedicated to crystallography and small-angle scattering for cutting-edge structural biology investigations.

The ABF is a consortium of seven national laboratories funded by DOE’s Bioenergy Technologies Office. Its mission is to develop biomanufacturing tools, processes, and partnerships that enable sustainable industrial production of renewable fuels and chemicals for the nation.

The CCI develops technology and software to improve the speed and ease of molecular structure solving using X-ray crystallography, neutron diffraction, and electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM) datasets.
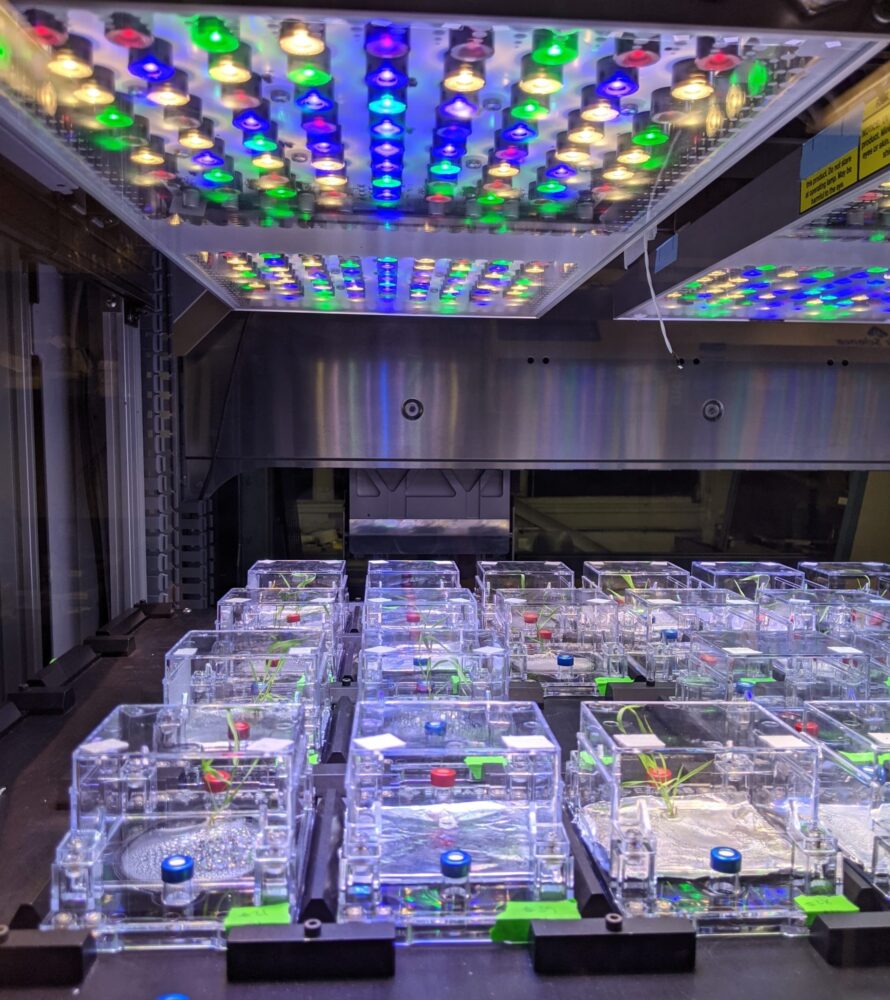

The EcoBOT is able to perform “self-driving experiments.” This all-in-one station enables researchers to compare their data while studying how plant genes and interactions between organisms affect ecosystem level processes.
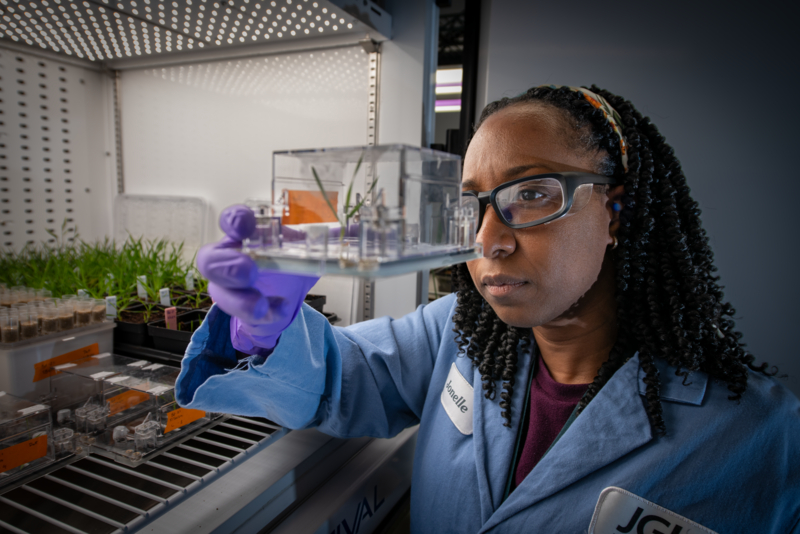

Led by EGSB, EcoFAB involves close collaborations with researchers at the DOE Joint Genome Institute and in the Earth and Environmental Sciences Area. A cross-functional team of biologists, geologists, and ecologists from Berkeley Lab will provide critical new insights into ecosystem processes through the creation of controlled model ecosystems in which microorganisms and host responses can be monitored in response to additional or changing variables.
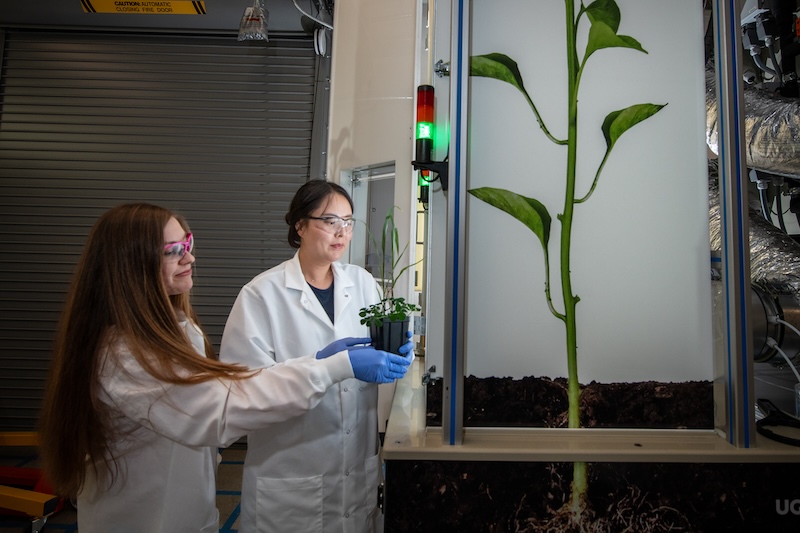

EcoPODs are enclosed environments that allow direct and intensive monitoring and manipulation of replicated plant-soil-microbe-atmosphere interactions over the complete plant life cycle. These several-cubic-meter, “pilot-scale” ecosystems are designed to bridge the gap between small, lab-scale experiments that are not large enough to mimic the environment and field-scale experiments that cannot be carefully controlled. The goal is to develop cross-disciplinary partnerships that will use the EcoPODs to develop testable ecosystem models in topics that include carbon cycling and secure biosystems design.
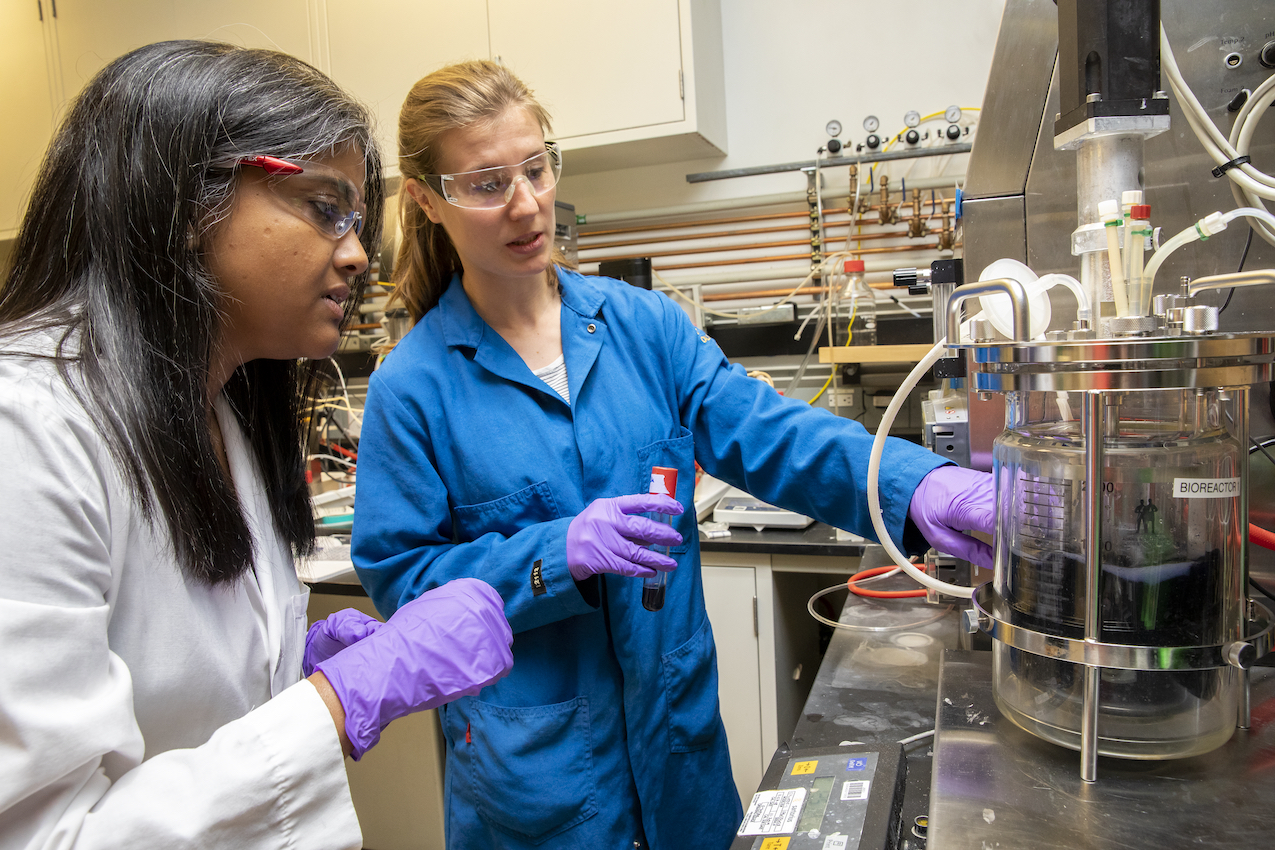

JBEI researchers are using the latest tools in molecular biology, chemical engineering, and computational and robotic technologies to transform biomass into biofuels and bioproducts.
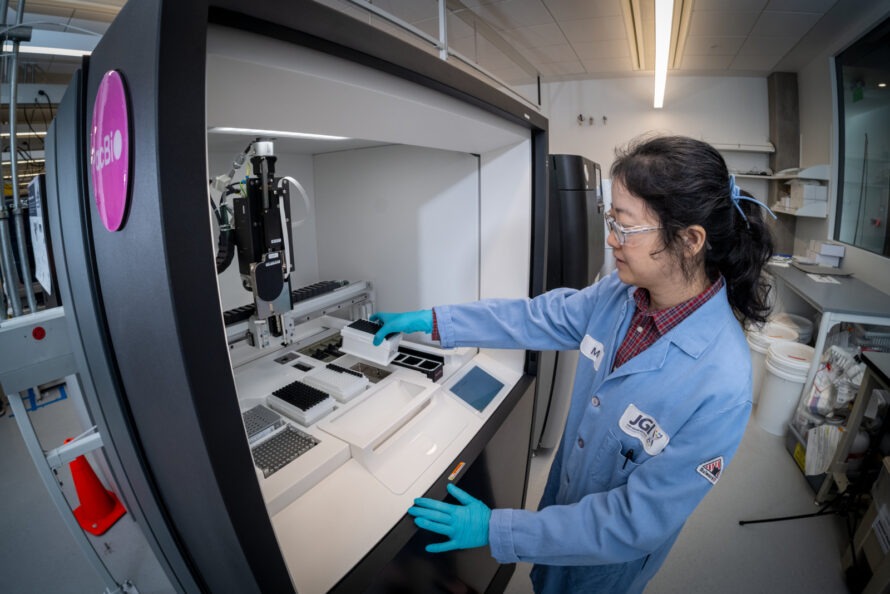

Advances genomics in support of U.S. Department of Energy missions related to energy generation and environmental characterization and cleanup.
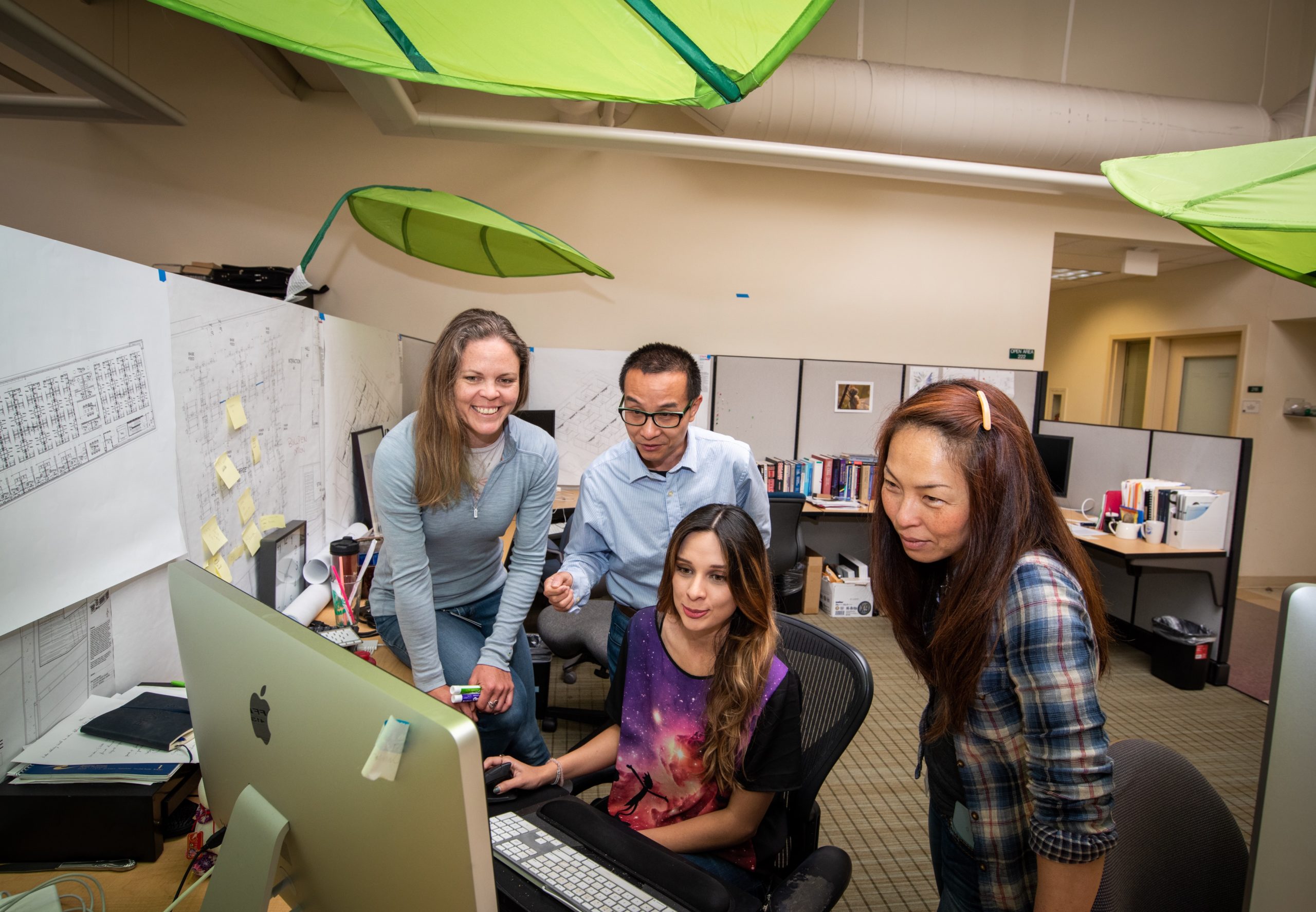

KBase is an open platform for comparative functional genomics and systems biology for microbes, plants and their communities, and for sharing results and methods with other scientists. Berkeley Lab is the lead institution in a partnership comprised of Argonne, Brookhaven, and Oak Ridge National Laboratories.
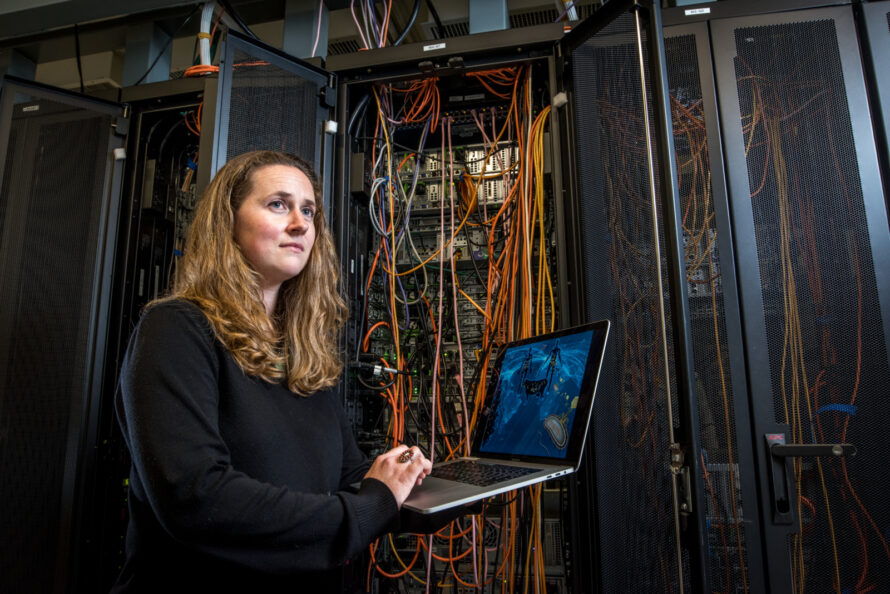

A multi-national laboratory partnership led by Berkeley Lab, NMDC seeks to address fundamental roadblocks in microbiome data science and gaps in transdisciplinary collaboration. Its two strategic priorities—infrastructure and engagement—and future activities support the long-term vision of empowering the research community to more effectively harness microbiome data.
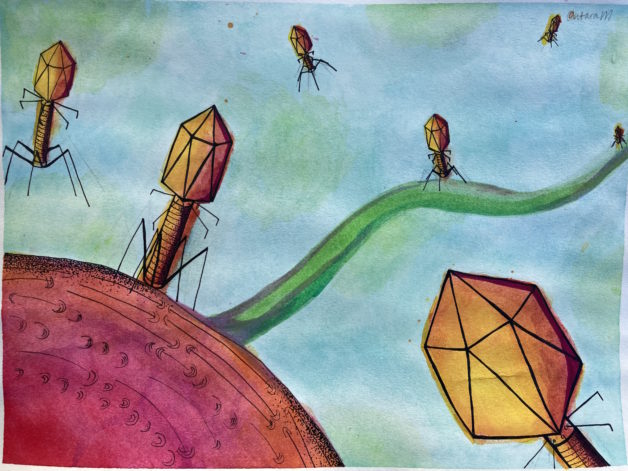
The Phage Foundry is a high-throughput platform for rapid design and development of countermeasures to combat emerging drug-resistant pathogens.
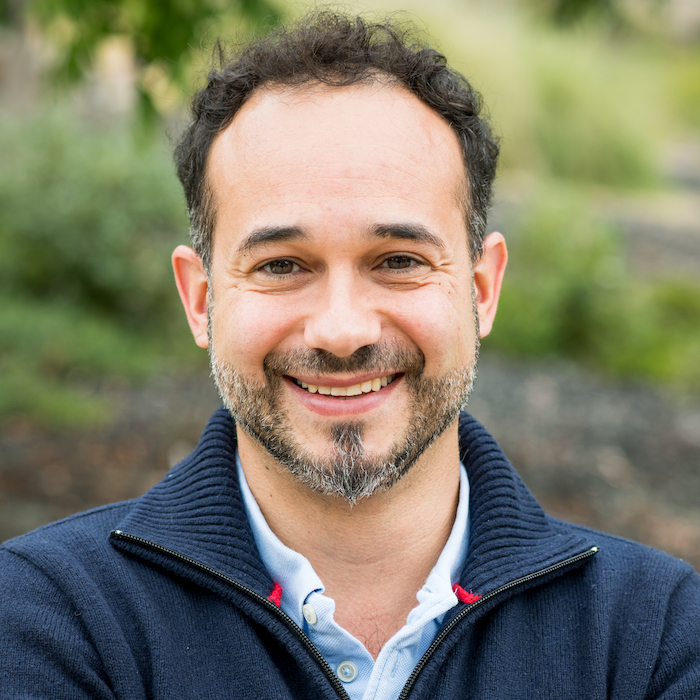


Héctor García Martín, a staff scientist in the Biological and Systems Engineering Division, is working to accelerate and refine the synthetic biology landscape by applying artificial intelligence and the mathematical tools he mastered during his training as a physicist.