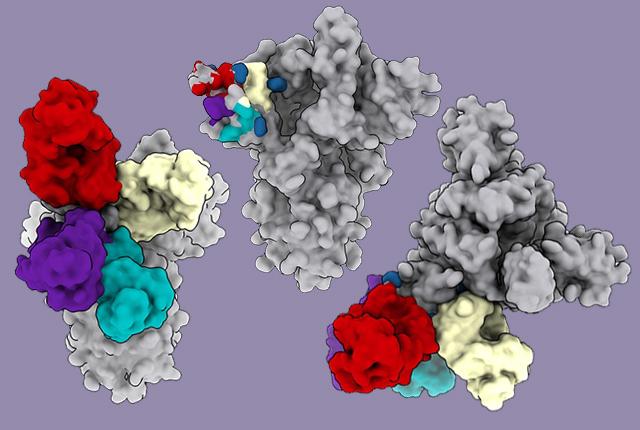
Scientists at the Berkeley Center for Structural Biology (BCSB) contributed resources and data to a recently-published study revealing a new site on the coronavirus spike protein used by antibodies to block the invasion of the virus into healthy cells. Despite less being known about this newly-identified site, dubbed the N-terminal domain, this study has shown that antibodies attached to this region triggered a potent immune response.
The main author of this study, David Veesler of the University of Washington’s School of Medicine, used the BCSB beamline 5.0.2 at the Advanced Light Source to determine the crystal structure, or 3D arrangement of molecules, of the N-terminal domain.
The discovery of this new antibody binding site will help scientists as they work to continue improving treatment and vaccine formulations for COVID-19 and its variants.
Read the UW press release.