 Recently, scientists from University of California, San Francisco, performed research at two national laboratories to determine protein structures that could be the key to preventing
Recently, scientists from University of California, San Francisco, performed research at two national laboratories to determine protein structures that could be the key to preventing 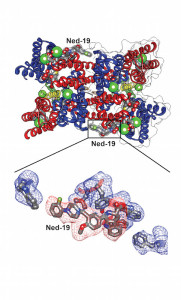 Ebola infection. Alexander Kintzer and Robert Stroud, used two structural biology beamlines (5.0.2 and 8.3.1) at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source, to determine in atomic detail how a potential drug molecule fits into and blocks a channel in cell membranes that Ebola and related “filoviruses” need to infect victims’ cells. The study, published March 9 in Nature, marks an important step toward finding a cure for Ebola and other diseases that depend on the channel. Read more at the SLAC News Center. This work has been highlighted by the ALS.
Ebola infection. Alexander Kintzer and Robert Stroud, used two structural biology beamlines (5.0.2 and 8.3.1) at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source, to determine in atomic detail how a potential drug molecule fits into and blocks a channel in cell membranes that Ebola and related “filoviruses” need to infect victims’ cells. The study, published March 9 in Nature, marks an important step toward finding a cure for Ebola and other diseases that depend on the channel. Read more at the SLAC News Center. This work has been highlighted by the ALS.