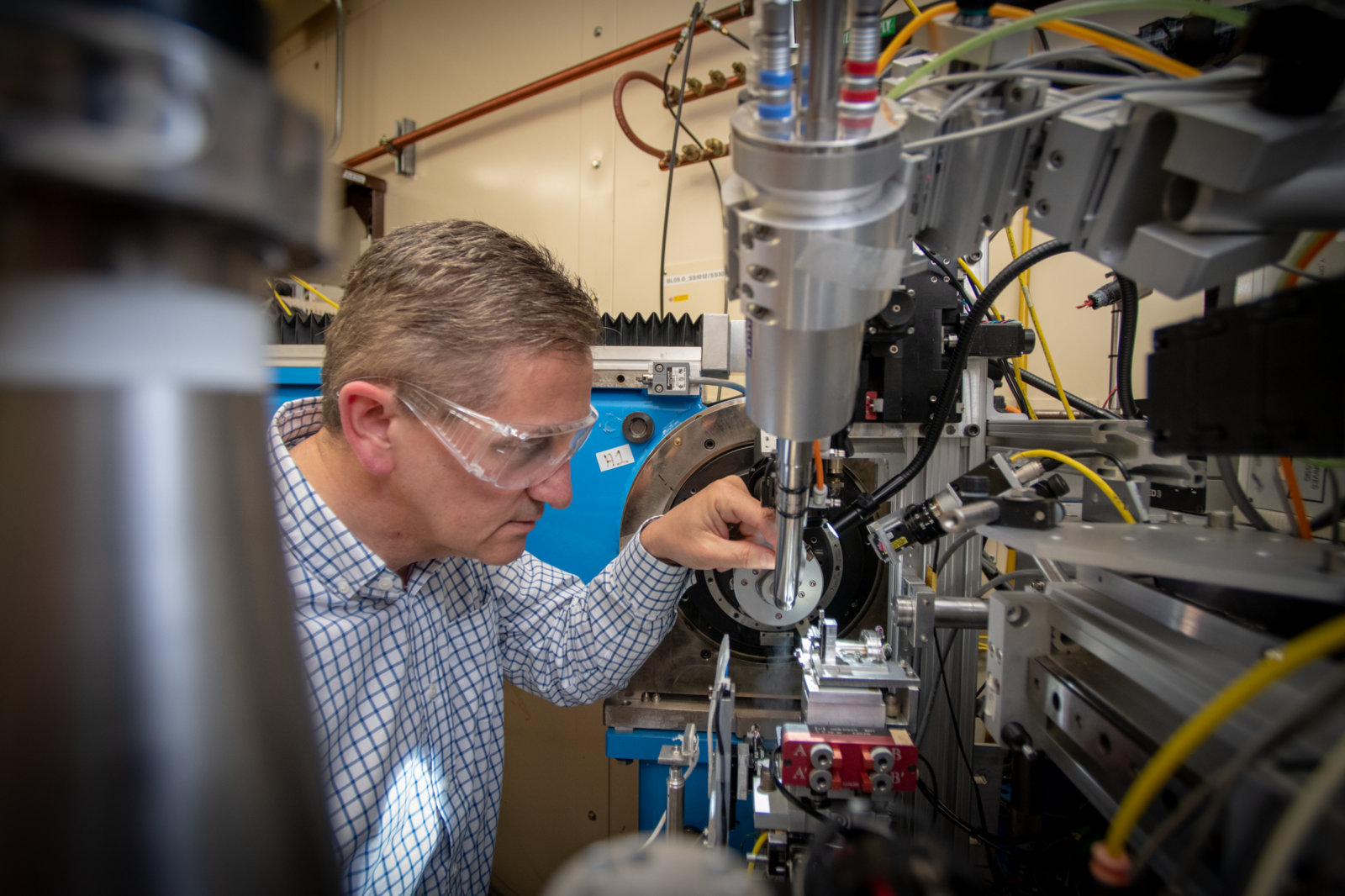
The ALS-ENABLE program integrates existing synchrotron structural biology resources at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source (ALS) to better serve researchers. Our scientists guide users through the most appropriate routes for answering their specific biological questions.

Located at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source (ALS), the BCSB runs five beamlines optimized for macromolecular protein crystallography.
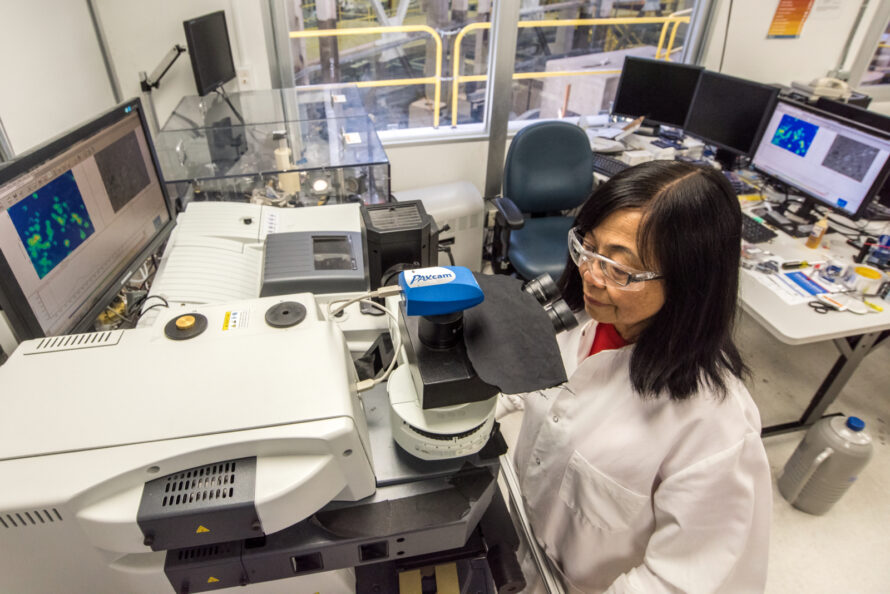

BSISB develops state-of-the-art infrared instrumentation and techniques for characterizing and imaging interactions among plants, microbes, and the environment.

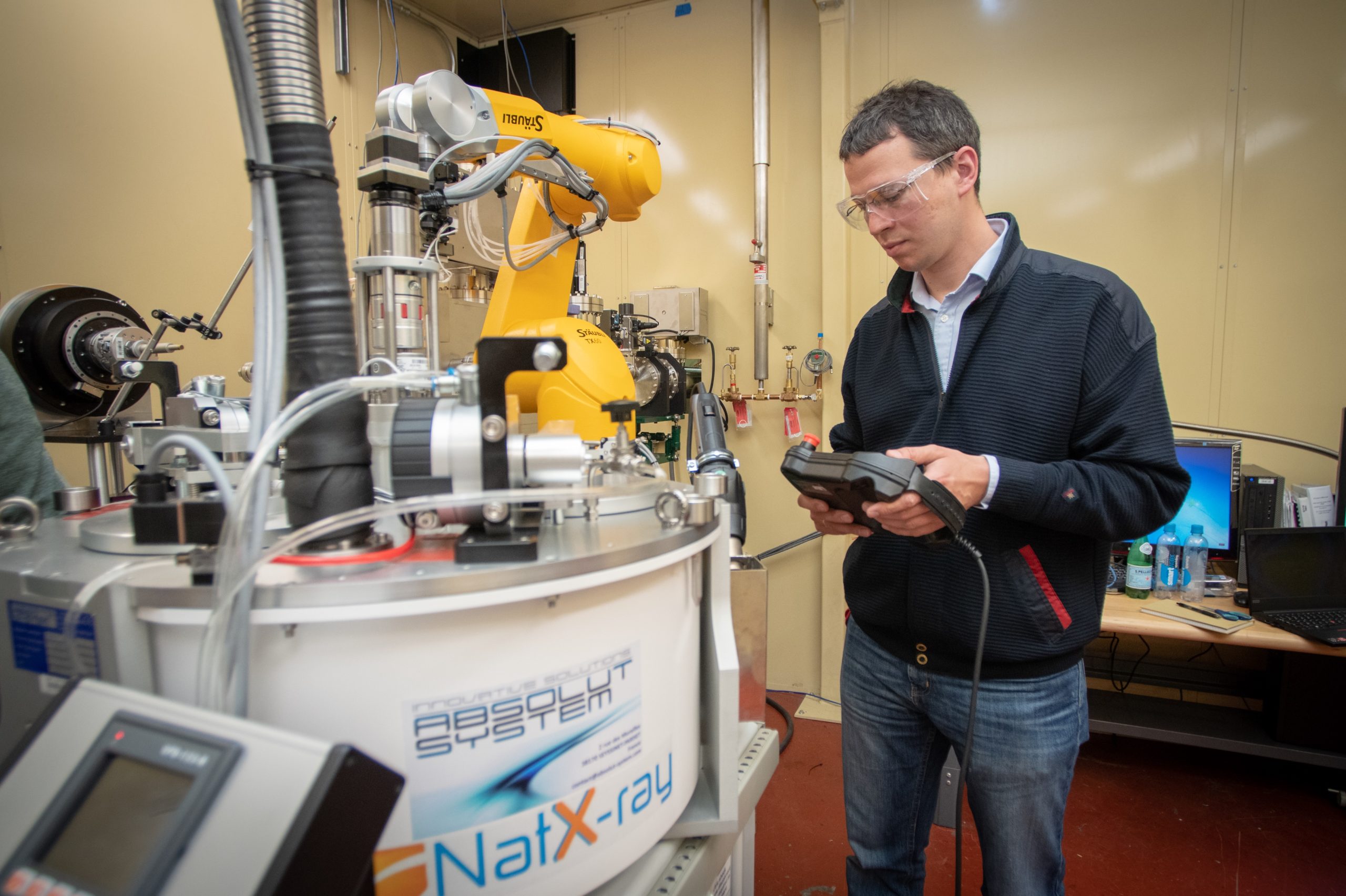
CCI develops new computational algorithms and tools for structural biology, in particular automated macromolecular crystallography, neutron crystallography, free electron laser data processing, and methods for automated diffraction data analysis.

NCXT is a joint effort between UC San Francisco and Berkeley National Lab to establish an X-ray microscope to perform computed tomography (aka CAT) scans of biological cells and develop other capabilities for cell and molecular biology studies.

PET@LBNL, or “petal,” scientists excel in the evaluation, validation and application of early-use positron emission tomography (PET) tracers.

SBDR is a multi-investigator, multi-institutional, interdisciplinary effort optimized to meet the extreme challenges of characterizing transient complexes and conformations acting in DNA repair responses. The program will integrate knowledge of DNA repair proteins and pathways by analyzing keystone complexes functioning as regulatory nodes in complex cellular responses to DNA damage.

Supported by the U.S. Department of Energy and the National Institutes of Health, the SIBYLS beamline (12.3.1) at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source (ALS) is optimized for both small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and macromolecular crystallography (MX), making it unique among the world’s mostly SAXS- or MX-dedicated beamlines.
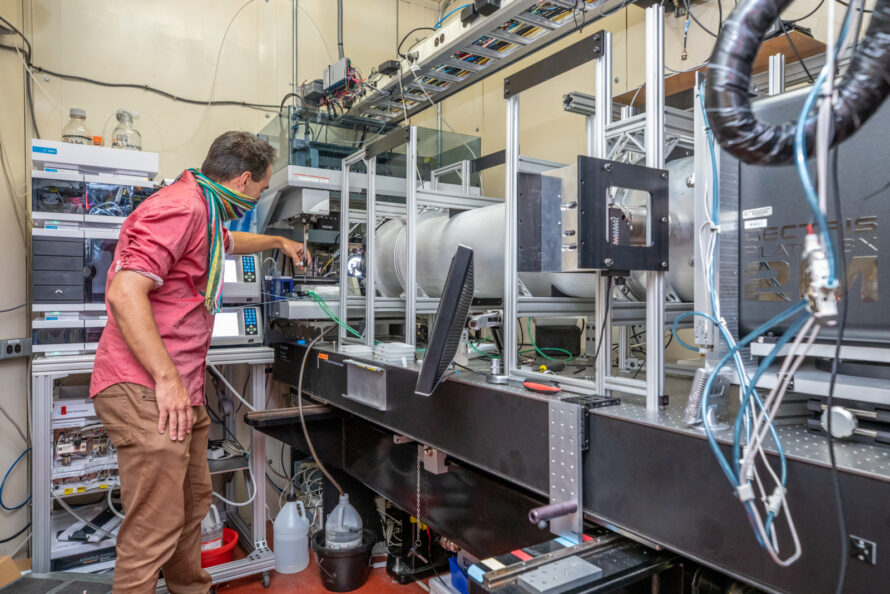
During the pandemic, a team of structural biologists at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source (ALS) supported “Task 5” of DOE’s National Virtual Biotechnology Laboratory, which was developing antibody-based diagnostics. Taskforce 5 will continue to advance capabilities at the ALS and two other DOE Office of Science user facilities to develop and test three plug-and-play integrated DOE bioimaging data pipelines for rapid invention of therapeutic, diagnostic, and vaccine countermeasures against emerging biothreats.

CAMERA is a coordinated team of applied mathematicians, computer scientists, light scientists, materials scientists, and computational chemists focused on targeted science problems, with initial involvements aimed at the Advanced Light Source (ALS), Molecular Foundry, and National Center for Electron Microscopy (NCEM). The goal is to accelerate the transfer of new mathematical ideas to experimental science.
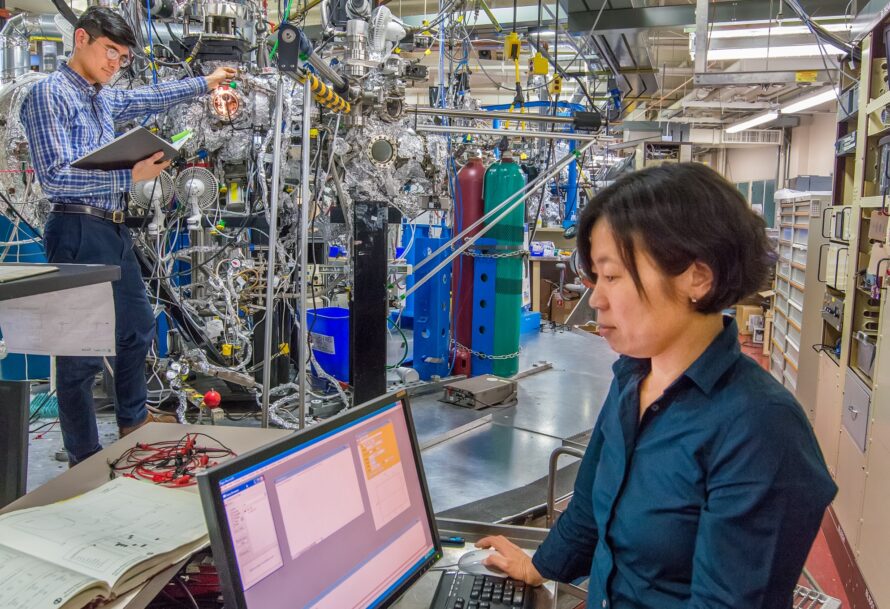
The mission of LiSA is to directly produce liquid fuels by artificial photosynthesis, using only sunlight and components of air, water, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen. The initiative focuses on establishing the science principles by which coupled microenvironments used for catalysis, transport, and light capture can be co-designed to achieve high efficiency and selectivity for the desired products.



