Data collected at the Berkeley Center for Structural Biology (BCSB) in the Advanced Light Source (ALS) has provided new structural insights into an antibody that protects against the bacterium that causes meningitis and sepis; a protein that unwinds quadruple DNA/RNA helixes; and an antibody targeting interleukin-2 that may provide a means of treating autoimmune disorders.
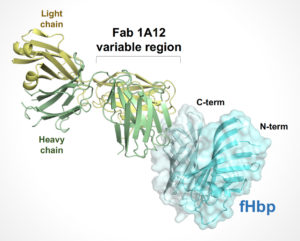
A team led by researchers at UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospital and GlaxoSmithKline performed high-resolution protein crystallography at ALS beamline 5.0.1 to determine the structure of a human antibody that broadly protects against a bacterium that causes meningitis and sepsis. The work, reported in a paper published in Nature Communications, provides molecular-level information about how the antibody confers broad immunity against a variable target and suggests strategies for further improvement of available vaccines.
For more, read the ALS Science Highlight.
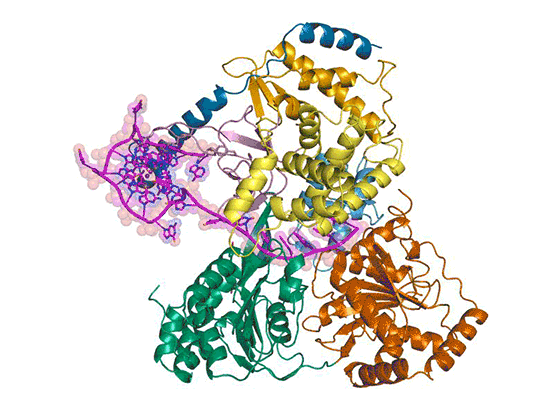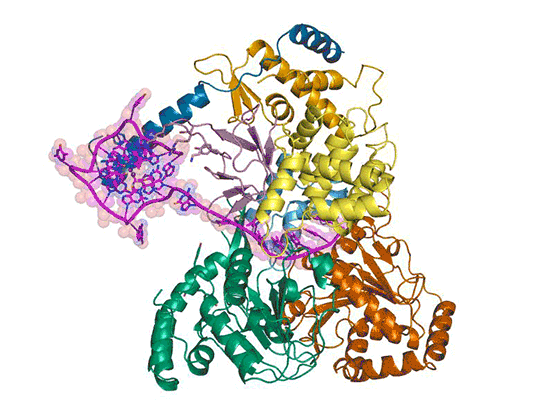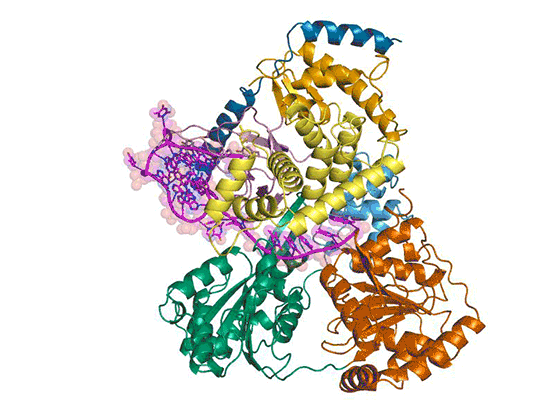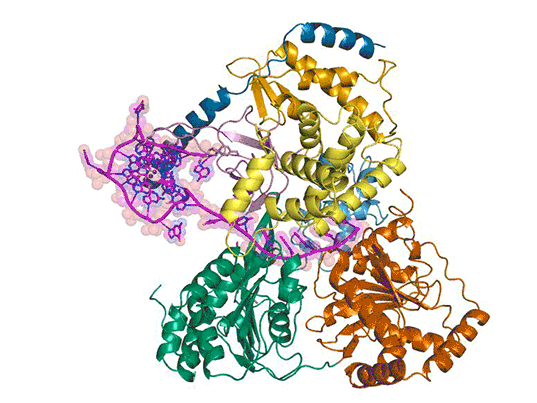
Also utilizing beamline 5.0.1, a team led by researchers at the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute and Cambridge University visualized the unfolding of a G-quadruplex, a quadruple-helix structure that guanine-rich DNA and RNA sequences can fold into, by a protein called DHX36. The work, reported in a paper published in Nature, provides a potential target for drug development.
For more, read the ALS Science Brief.
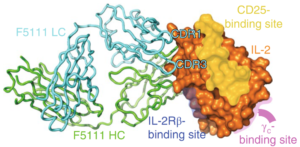
Researchers found a way to better control IL-2 signaling by identifying an antibody (F5111) that locks it in a conformation that preferentially activates regulatory cells.
A team led by researchers at UC San Francisco and Pfizer performed protein crystallography at ALS beamline 8.2.1, to identify a human antibody that locks the signaling protein interleukin-2 into a conformation that preferentially activates regulatory T-cells. The work, reported in a paper published in Nature Medicine, suggests an approach to treating autoimmune diseases by restoring the balance between two types of white blood cells.
For more, read the ALS Science Brief.
The ALS is a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Scientific User Facility operated by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. The BCSB is a national user facility operating under aegis of the Biosciences Area’s Molecular Biophysics and Integrated Bioimaging (MBIB) Division.