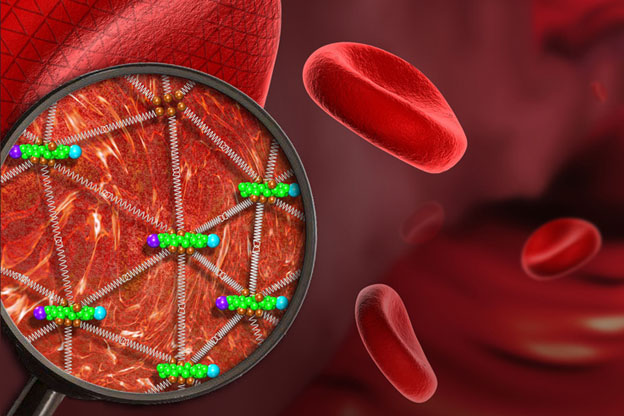
 Ke Xu, faculty scientist in the Molecular Biophysics and Integrated Bioimaging Division, used super-resolution microscopy to reveal the geodesic mesh supporting red blood cells, enabling them to be sturdy yet flexible enough to squeeze through narrow capillaries as they carry oxygen to tissues. The discovery could help uncover how malaria parasites hijack this mesh and destroy red blood cells. Read more at UC Berkeley News.
Ke Xu, faculty scientist in the Molecular Biophysics and Integrated Bioimaging Division, used super-resolution microscopy to reveal the geodesic mesh supporting red blood cells, enabling them to be sturdy yet flexible enough to squeeze through narrow capillaries as they carry oxygen to tissues. The discovery could help uncover how malaria parasites hijack this mesh and destroy red blood cells. Read more at UC Berkeley News.