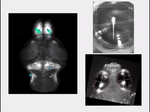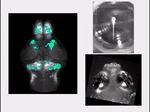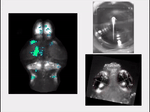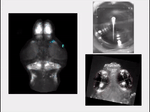
Brain-wide activity in a zebrafish when it sees and tries to pursue prey. (Credit: Isacoff lab, UC Berkeley)
Ehud Isacoff of the Molecular Biophysics and Integrated Bioimaging (MBIB) Division is the project lead on a $21.6 million grant awarded to UC Berkeley as part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency’s (DARPA’s) Neural Engineering System Design program. The team led by Isacoff, director of the Helen Wills Neuroscience Institute at UC Berkeley, aims to develop a novel brain-machine interface that uses light to monitor and modulate the activity of thousands to millions of individual neurons in the cerebral cortex.
To communicate with the brain, the team will first introduce a gene encoding a fluorescent protein into neurons, making the cells flash when they fire an action potential. This will be accompanied by a second gene encoding a light-activated protein that stimulates neurons in response to pulses of light. The reading device Isacoff’s group is developing is a miniaturized light field microscope, which captures light through an array of lenses and reconstructs images computationally in any depth of focus. For the writing component, they are developing a means to stimulate groups of neurons by projecting three-dimensional light patterns onto them.
The researchers’ goal during the initial four-year funding period is to create a prototype device using model organisms—such as zebrafish larvae and mice—in which neural activity and behavior can be simultaneously detected and controlled. But DARPA’s ultimate goal is to accelerate the development of biocompatible neural implants for use in humans to compensate for sensory deficits or to control prosthetic devices. Read more from the UC Berkeley News Center.



